Isochronic tones and Binaural beats are the most likely terms you are hearing for the first time today or had come across but had no idea how they factor into meditation and personal well-being. You are not alone in this because even those who have an idea of what these two mean and how they can enhance your meditation experience or personal growth may still find it challenging to determine which one is the better option.
To make ends and tails of the Isochronic tones and Binaural beats debate, you first need to understand the overarching principle or force behind them, which is brainwave entrainment. Isochronic tones and binaural beats are some of the techniques used to achieve brainwave entrainment.
Brainwave Entrainment – What is?
Brainwave entrainment is how the brain is stimulated into a different state by using stimuli like light, sound, or even an electromagnetic field. The stimulus targets one part of the brainwaves aiming to synchronize them with its beat. Your brainwaves vary depending on your emotion and activity.
The dominant brainwaves determine our state, so if the slower brainwaves become dominant, you will tend to be sluggish and dreamy. On the other hand, when the higher and faster frequencies are dominant, we become alert and more active. There are five types of brainwaves;
- Gamma Brainwaves from 32-100Hz are the fastest measurable waves. They are associated with increased perception, problem-solving, and take your brain to a peak mental state.
- Beta Brainwaves begin from 13 – 32Hz. They are associated with the normal state of consciousness and active thinking. It is the state used when having a conversation or learning a new concept.
- Alpha Brainwaves range from 8 -13 Hz, and they were the first ones to be discovered, and they are easily observed. They are active when you are relaxed physically and mentally, such as when you are just about to sleep, doing yoga, or when being creative and productive.
- Theta Brainwaves are detected in the 4 – 8 Hz range and is active when we are in deep relaxation. It influences our creativity state, reduced consciousness, insight, and dreams.
- Delta Brainwaves are the slowest of all brainwaves. They range from 0.5 Hz to 4 Hz and is available in the deep sleeping and dreaming state. In this therapeutic sleep state, is where healing and rejuvenation happens.
The synchrony and entrainment of the brainwaves to the stimulus signal is known as Frequency Following Response, which works in the same manner as natural synchronization, seen in tuning forks, fireflies, pendulum clocks, and brainwave activity.
Related reading: What Happens When You are in Deep Meditation? – Opens in new tab.
What Are Isochronic Tones?
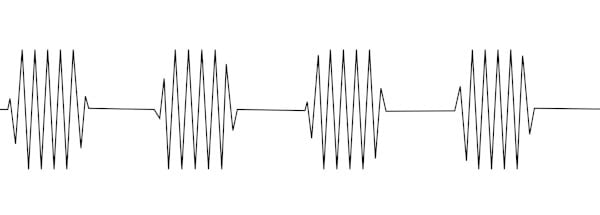
Isochronic tones are an audio form of entrainment. They are regular beats on one tone, usually embedded in other sounds, say nature sounds and music ones. They are set to pulsate on and off at intervals spaced evenly. In between, the intervals are silent pauses, and these serve to create a rhythmic pulse.
The number of pulses for every second indicates the frequency. For example, 8Hz will be 8 of the tones per second. Isochronic sounds are said to have one of the most potent entrainment effects on your brain.

How Isochronic Tones work?
Isochronic tones work by exciting the thalamus part of the brain, which makes their stimulation stronger. They can target any brainwave frequency depending on the state that you desire to induce. The targeting is done by varying the speed of the pulses. If you want a low frequency, the sound will be turned on and off slowly while the pulsating will be much faster when targeting a higher brainwave frequency.
By embedding the isochronic tone in music or natural sounds, one frequency band will be oscillating while the rest of the music stays unaffected. When the embedding is done well, isochronic tones may not be noticeable to the ear.
How they sound?
Isochronic tones have a monotonous sound and but at the same time, they are intermittent since they keep being turned on and off. They have a sharp distinctive sound when alone but usually hide behind the music and natural sounds they are placed inside.
You do not need headphones to listen to them though it helps, especially if you are looking to be in perfect alignment with the sound from both sides of your head.
Listen to the sample of the Isochronic tones below. You don’t need headphones.
Ruji Chapnik (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)
What are Isochronic Tones used for?
The fact that isochronic tones can be used to induce different mental states means they can be used for various purposes, including the following;
- It helps in relieving stress and anxiety. Stress and agitation and anxiety are all states that are accompanied by high beta brainwave levels. Using low beta or even alpha frequency isochronic tones, you can lower the dominant frequency reducing stress levels.
- They are used to induce meditation and deep relaxation. When relaxation is required or when people seeking to be calm or need to meditate, especially for those still learning meditation, using isochronic tones can help activate alpha and theta frequencies, which will help you relax.
- It is used to increase focus, cognitive abilities, and memory. Using isochronic tones can help get your mind in an optimal state to focus until the duration is up. Stimulating the Alpha brainwaves is also helpful in improving memory and the ability to retain information.
- Isochronic tones can be used to improve the quality of sleep by stimulating the lower frequency brainwaves such as low delta frequency while at the same time reducing the dominance of beta frequencies, which allow you to get into a deep sleep.
- They can offer you energy and motivation when feeling lethargic. By activating higher amounts of gamma and beta activity, you can boost your energy levels and maintain alertness. People use isochronic tones as an effective alternative to caffeine and other chemical stimulants without their side effects.
What are the benefits of isochronic tones?
Research on the benefits and effects of isochronic tones has been limited, with many focusing on general brain entrainment or combining both audio and visual means. The first point would be to understand whether isochronic tones can have actual results in brain entrainment.
That has been proven in several studies. One study identified that acoustic stimuli could result in brain synchronization, affecting cognitive abilities, which include focus, memory, etc.
A review of different studies indicates that brain entrainment aids with attention, sleep, mood enhancement, perception of pain, and alleviating stress and anxiety, among other things. In other studies, brainwave entrainment has been shown to help with headaches and migraines, premenstrual syndrome.
Pros & Cons
Isochronic tones present new opportunities with few limitations. Its benefits include;
Pros
- You do not need headphones to listen to the sounds
- They result in fast and powerful results as they target the temporal lobe
- They are effective at improving IQ and concentration
- Allow for group sessions
- It is excellent for people who want to hear the sound loud and its effect in the ears.
Cons
- The sound may be uncomfortable for several people
- Requires the tone to be audible in the record for effective entrainment
- It does not make for proper entrainment, especially in the lower frequency ranges.
How long should I listen to Isochronic Tones?
You will need to determine your sensitivity before taking full isochronic therapy because everyone reacts differently. However, for starters, you should limit your sessions to just 15 minutes or even less if you are going to combine audio/visual entrainment.
Are They Safe?
Isochronic tones are generally safe for use. They are not associated with any side-effects you would find in chemical stimuli and even visual entrainment, which may cause seizures for epileptic people. However, caution must be exercised regarding the following aspects;
- Use of loud volume can be harmful to your ears, so keep the levels reasonable below 70 decibels, i.e., not above the normal conversation levels.
- You should not use isochronic tones if you have hyperarousal or symptoms associated with instability like bipolar attacks, hyper-vigilance, spasticity, and other impulsive behavior.
- Should you find yourself experiencing dizziness, increased heartbeat, and convulsions, you should stop using isochronic tones both immediately and permanently.
Take a look at these Isochronic Tones recordings. Choose the one that suits you best. Opens in new tab
What are Binaural Beats?
Binaural beats are another form of audio brainwave entrainment technique. Like isochronic tones, they depend on soundwaves only differing in their application of the technology. Essentially, a binaural beat is an auditory illusion.
Two tones of different frequencies are fed into each ear to create a binaural beat. However, the brain- instead of listening to two different tones, works out the difference between the two tones and falls in synchrony with that. Hence, the tone you are listening to does not exist. In reality, it has just been created by the brain.
Another difference with isochronic tones is that binaural beats tones, although different, are continuous and not intermittent like isochronic tones.

How binaural beats work?
Because they depend on two different sounds, you have to use headphones so that each ear gets a different frequency tone. For binaural to work, the tones need to be under 1000 Hz each, and the difference in their frequency should not be more than 30 Hz.
So if the right ear is getting a 300 Hz frequency and the left ear is receiving a tone a frequency if 315 Hz, the brain will process the two frequencies as one 15Hz frequency, which is the difference between the two. It starts synchronizing its brainwaves to follow that of the binaural beat through a frequency following response.
How they sound?
Binaural beats are usually comfortable to the ear. Their low pitch and lower amplitude mean they are not as distinctive to the ear as isochronic tones.
They can also be layered with music and other sounds making for great entertainment. You will, however, need a stereo headphone set since on loudspeaker they become monoaural.
Use your headphones to listen to the sample of Binaural beats below.
What are binaural beats used for?
Binaural beats are used to create the same brainwave entrainment effect. They are usually targeted to reduce anxiety, increase concentration and focus, improve mood, pain management, and relaxation.
Binaural beats ranging from 1 to 30 Hz have been suggested to have the same effect as meditation. Like isochronic tones, the binaural beats used are determined by the mental state you want to create. For example,
- If you’re going to create a deep sleep and relaxed state, you have to target the delta brainwaves with binaural beats ranging from 1-4 Hz.
- For REM sleep, reduced anxiety, and improved meditation and creativity, you will be looking to entrain the ranges in theta brainwaves from 4 – 8Hz.
- If you want to increase positivity and decrease anxiety and encourage relaxation, you will need to use binaural beats ranging from 8 – 13Hz to target the alpha brainwaves.
- To target the beta brainwaves responsible for increased concentration, alertness, improved memory, and problem-solving, you need to use binaural beats in the 14 – 30Hz.
What are the benefits of binaural beats?
Binaural beats offer several benefits backed by research considering they have been around for far much longer than isochronic tones from the 1800s. Thus, they have had enough time to be studied to establish their effect on the brain and different states.
Several studies have found that binaural beats help with anxiety and pre-operative anxiety. Other studies indicated the beats have a calming effect similar to that of meditation to aid in relaxation.
A recent 2019 review of 22 studies also established that binaural beats greatly affect anxiety, pain management, and relaxation. From these effects, the technique can also be used to improve your sleep quality and general quality of life.
Pros & Cons
Pros
- It has been around long enough to be tried and tested for effectiveness
- Devices and tones are easily affordable compared to other brainwave entrainment methods
- There is a large number of beats to pick from
- Effective even on delta brainwaves
- Allows for a discrete experience
- They are comfortable to the ear
Cons
- They have a low presence, which may be difficult to detect for those who prefer beats to listen to.
- It may take time for the entrainment to take effect.
- You will need to have headphones.
How long should I listen to binaural beats?
The same precautions taken with the isochronic tones also apply here. The experience depends on the individual, but beginners should not go further than 15 minutes, and with time, you will settle on a comfortable and effective duration.
Take a look at these Binaural Beats recordings. Choose the one that suits you best. Opens in new tab
Are They Safe?
Binaural beats are generally safe without any side effects. Occasionally, individuals may experience headaches after prolonged use. You may also have your hearing affected if you listen to the beats at volumes above 70 decibels. Binaural beats are a safe option without the side effect associated with chemical stimulants.
Isochronic vs. Binaural – Which is better?
| Isochronic Tones | Binaural Beats | |
|---|---|---|
| Use of headphones | Not needed | Headphones required |
| Use on loudspeakers | Can be played on speakers | Becomes monoaural when on speakers |
| Pitch | Has a higher pitch | Lower pitch |
| Ease on ears | Can feel intense and sharp to the ears | Comfortable and smooth to the ears |
| Volume | High volume | Lower in volume |
| Number of tones | One intermittent tone | Two tones at different frequencies |
| The time before entrainment starts | Brainwave entrainment happens faster | Takes time for entrainment to take effect |
| How long the effects last | Effects last a bit longer | Requires more training to extend the entrainment effect |
| Amount of research | Little research has been done on its effectiveness | Plenty of research and tests have been conducted to prove effectiveness and use |
| Cost | Tones and devices are expensive | Plenty of free beats and more affordable quality beats |
| Availability and diversity | Range of toes for use is limited | Readily available with a wide variety to pick from |
♦ If this article resonates with you, please join our newsletter by using the forms on this website so we can stay in touch.
Stay in Touch
 Join our newsletter by using the forms on this website or click here!
Join our newsletter by using the forms on this website or click here! Follow us on Google News
Follow us on Google News Follow us on Facebook
Follow us on Facebook
Featured Image by Gerd Altmann from Pixabay